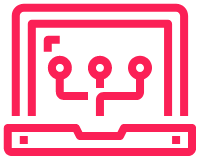
I have used RPA web automation to get the days exchange rates for five currencies. This is a quick example of what is possible. A lot more can be done with this and it’s so simple to use.
All my RPA scripts can be found in my Github
The process of the script is;
1. Open chrome and go to https://www.x-rates.com/table/?from=USD&amount=1
2. Pick out the currencies; Euro, GBP, AUD, CAD and Yen in the table#
3. Print out those rates in the console
4. Close Chrome
5. Add the currencies to a dictionary and list
6. Write that list to a CSV file
Script
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
import rpa as r import os import csv basedir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) def write_csv(write_file, data_list): # Output with open(write_file, "w", newline="") as f: csv_writer = csv.DictWriter(f, data_list[0].keys()) csv_writer.writeheader() csv_writer.writerows(data_list) print("CSV written out") r.init(True, True) r.url('https://www.x-rates.com/table/?from=USD&amount=1') r.wait(2.5) euro = r.read('//*[@id="content"]/div[1]/div/div[1]/div[1]/table[2]/tbody/tr[17]/td[2]/a') gbp = r.read('//*[@id="content"]/div[1]/div/div[1]/div[1]/table[1]/tbody/tr[2]/td[2]/a') aud = r.read('//*[@id="content"]/div[1]/div/div[1]/div[1]/table[1]/tbody/tr[4]/td[2]/a') cad = r.read('//*[@id="content"]/div[1]/div/div[1]/div[1]/table[1]/tbody/tr[5]/td[2]/a') yen = r.read('//*[@id="content"]/div[1]/div/div[1]/div[1]/table[1]/tbody/tr[9]/td[2]/a') print(f"\n1 USD buys: {euro} Euro") print(f"1 USD buys: {gbp} GBP") print(f"1 USD buys: {aud} AUD") print(f"1 USD buys: {cad} CAD") print(f"1 USD buys: {yen} YEN\n") r.wait(1) r.close() forex_list = [] forex_dict = {"Euro":euro, "GBP":gbp, "AUD":aud, "CAD":cad, "Yen":yen } forex_list.append(forex_dict) # Write Output write_file = f"{basedir}/forex.csv" write_csv(write_file,forex_list) |
Script Output Console
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
1 USD buys: 1.020248 Euro 1 USD buys: 0.892653 GBP 1 USD buys: 1.556548 AUD 1 USD buys: 1.370627 CAD 1 USD buys: 144.900664 YEN CSV written out |
Script Output CSV
|
0 1 2 3 |
Euro,GBP,AUD,CAD,Yen 1.020248,0.892653,1.556548,1.370627,144.900664 |
Extra Info
What I haven’t talked about yet is how I have made the script get the currencies I want. If we look at the web page we see a lot of currencies. How does RPA know which ones are which?
The answer is that the script is told what to read using Xpaths.
Useful link for identifying elements
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/kensoh_xpath-rpa-tagui-activity-6829673864633704448-Iw-D/
https://github.com/tebelorg/RPA-Python#element-identifiers
|
0 1 2 |
euro = r.read('//*[@id="content"]/div[1]/div/div[1]/div[1]/table[2]/tbody/tr[17]/td[2]/a') |
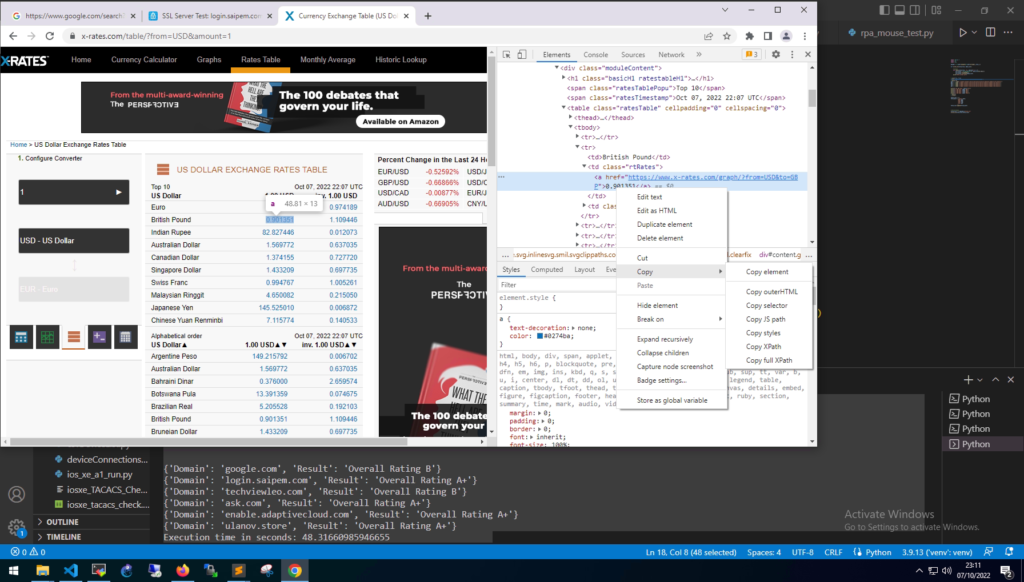
Othe rexamples of Xpaths are;
Google Search Box. This is searching the page for the name of “q”. And on the Google page this name is the search box.
|
0 1 2 |
//*[@name="q" |
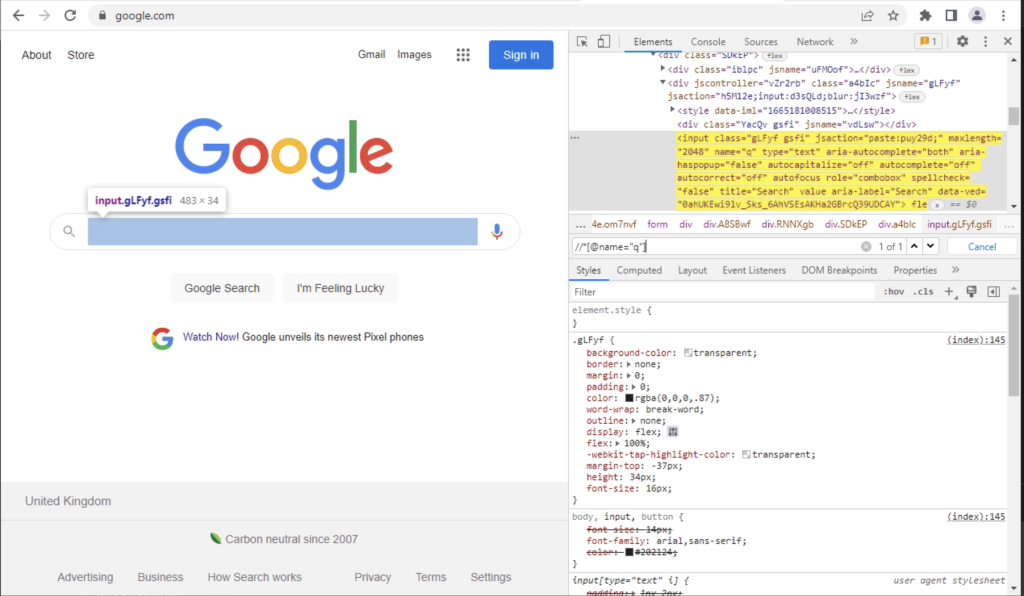
Another example is the search on SSL Labs. This is the exact same as Google, but this search bar is called “d”.
|
0 1 2 |
//*[@name="d" |