For this post, I wanted to just go through the NetBox setup and the ability to get started with automation.
Docker Compose
I will be using Docker for NetBox. There is an easy to get started version of NetBox using NetBox Docker
Install Docker
|
0 1 2 3 |
sudo apt update sudo apt install docker.io |
Download the Docker Compose binary from the official GitHub repo
|
0 1 2 |
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/latest/download/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose |
Apply executable permissions to the Docker Compose binary
|
0 1 2 |
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose |
Verify Install
|
0 1 2 |
docker-compose --version |
The commands for docker compose installed for me are docker-compose. The documentation for NetBox are docker compose. More on this in the NetBox install section.
NetBox Setup
As mentioned in the Docker Compose section of this post, I am going to be using NetBox Docker. This is the easiest way I think to get it working in a lab. On the GitHub repo there is a lot of information. The minimum required is to have Docker Compose installed, and to then run the following. Please note that my Docker Compose install is using docker-compose as the syntax and not docker compose
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
git clone -b release https://github.com/netbox-community/netbox-docker.git cd netbox-docker tee docker-compose.override.yml <<EOF version: '3.4' services: netbox: ports: - 8000:8080 EOF docker-compose pull docker-compose up |
To create an admin user, use the following command. This will ask you what you want the credentials to be.
|
0 1 2 |
docker-compose exec netbox /opt/netbox/netbox/manage.py createsuperuser |
That covers it, if you want the docker container to run in the background, use the -d flag to detach it.
|
0 1 2 |
netbox-docker$ sudo docker-compose up -d |
Setting Up API Token
To setup the API token, go to the web interface http://127.0.0.1:8000/, login with the credentials created in the setup and click the top right user icon and select the Admin cog.
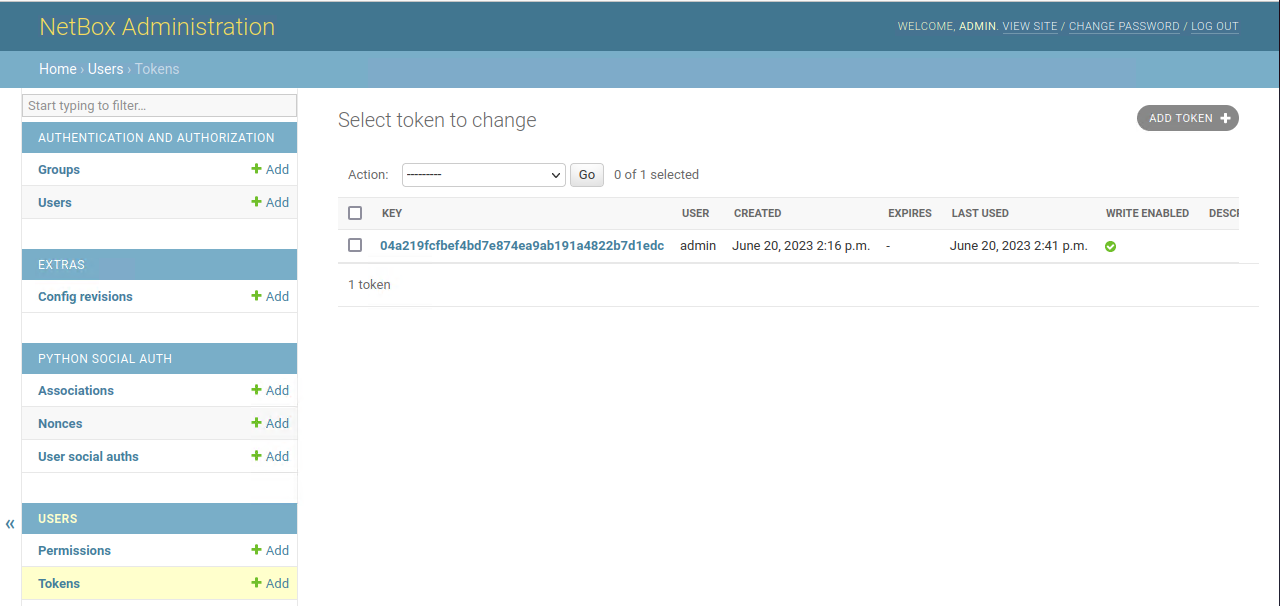
Once in here, this is the Django admin interface. Navigate to Users and Tokens.

Next click Add Token,
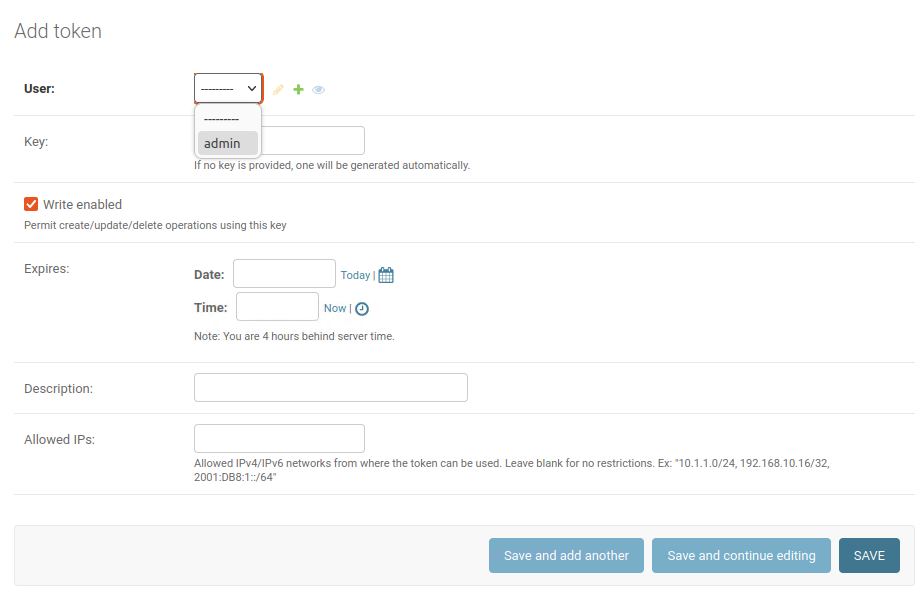
Select the user to create the token for. I only have admin available. Click save at the bottom and a token will be generated as shown in the screenshot above. Click on the key to go and copy it.
Adding Sites to NetBox
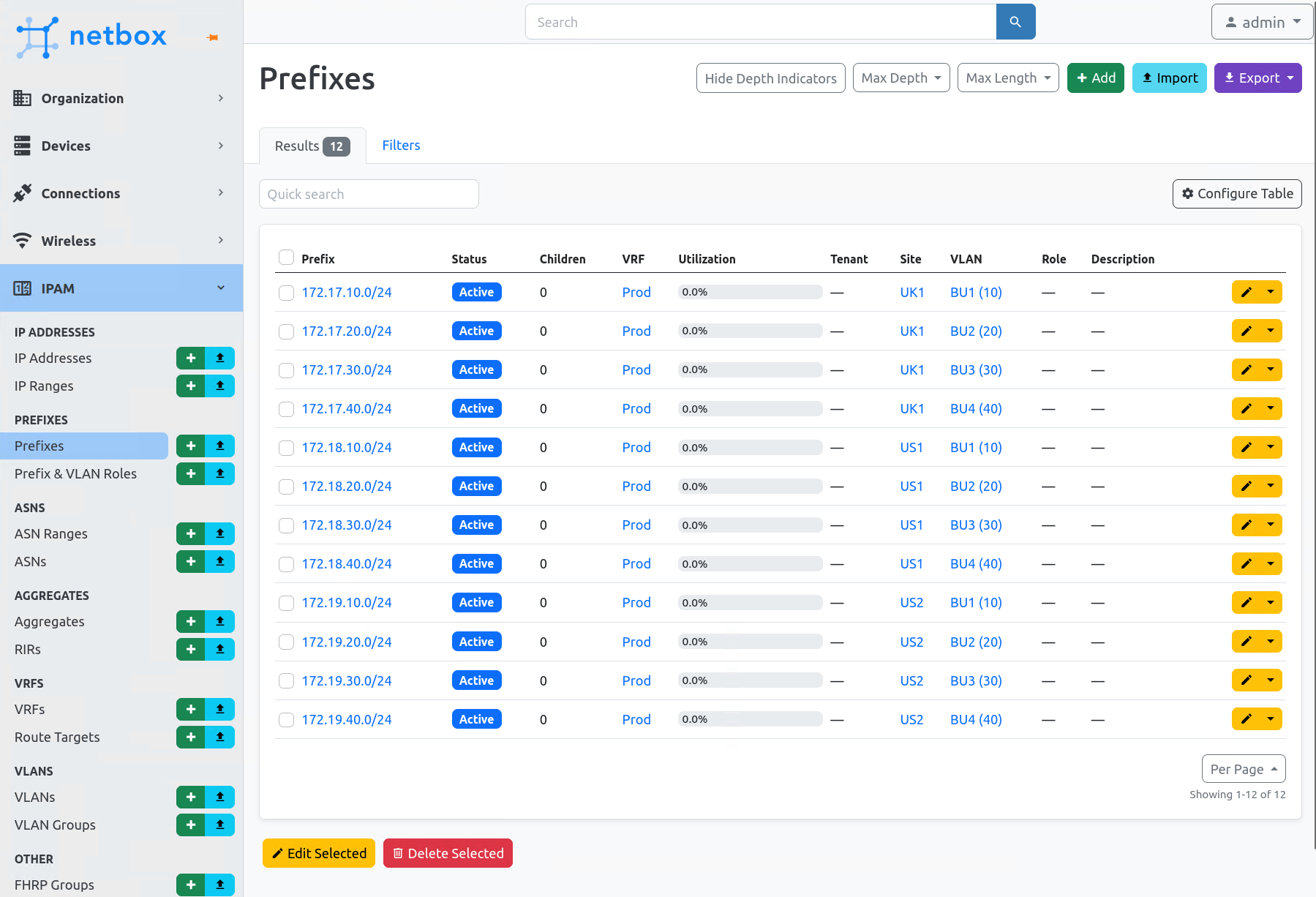
Now the API token has been setup we can almost start using the NetBox API. However, there isn’t anything in NetBox, so to go and manually a few things to NetBox, so we can search them with the API.
I have created the following in NetBox. This was very repetitive, easy to confuse and make mistakes during the process. But it will be automated soon.
- 3 Sites
- 2 VRFs per site
- 4 VLANs per site
- 4 Prefixes (Networks)
Getting Information from NetBox with PyNetBox
This basic script will output the site IDs and names of each site in NetBox
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import pynetbox # Instantiate a NetBox API object nb = pynetbox.api('http://127.0.0.1:8000', token='04a219fcfbef4bd7e874ea9ab191a4822b7d1edc') try: # Retrieve all sites from NetBox sites = nb.dcim.sites.all() # Process the sites for site in sites: print(f"Site ID: {site.id}") print(f"Name: {site.name}") print(f"Slug: {site.slug}") print('---') except pynetbox.core.query.RequestError as e: print(f"An error occurred: {e}") |
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
(venv) osboxes@osboxes:~/scripts/django-new_networks$ /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/venv/bin/python /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/pynetbox_getsites.py Site ID: 1 Name: UK1 Slug: uk1 --- Site ID: 2 Name: US1 Slug: us1 --- Site ID: 3 Name: US2 Slug: us2 --- |
The next script I have created is to get all VLANs in NetBox
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import pynetbox # Instantiate a NetBox API object nb = pynetbox.api('http://127.0.0.1:8000', token='04a219fcfbef4bd7e874ea9ab191a4822b7d1edc') try: # Retrieve all VLANs from NetBox vlans = nb.ipam.vlans.all() # Process the VLANs for vlan in vlans: print(f"VLAN ID: {vlan.id}") print(f"Name: {vlan.name}") print(f"VID: {vlan.vid}") print('---') except pynetbox.core.query.RequestError as e: print(f"An error occurred: {e}") |
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
(venv) osboxes@osboxes:~/scripts/django-new_networks$ /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/venv/bin/python /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/pynetbox_examples/pynetbox_getallvlans.py VLAN ID: 1 Name: BU1 VID: 10 --- VLAN ID: 2 Name: BU2 VID: 20 --- VLAN ID: 3 Name: BU3 VID: 30 --- VLAN ID: 4 Name: BU4 VID: 40 --- VLAN ID: 5 Name: BU1 VID: 10 --- VLAN ID: 6 Name: BU2 VID: 20 --- VLAN ID: 7 Name: BU3 VID: 30 --- VLAN ID: 8 Name: BU4 VID: 40 --- VLAN ID: 9 Name: BU1 VID: 10 --- VLAN ID: 10 Name: BU2 VID: 20 --- VLAN ID: 11 Name: BU3 VID: 30 --- VLAN ID: 12 Name: BU4 VID: 40 --- |
The next script is to get all the networks in NetBox.
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import pynetbox # Instantiate a NetBox API object nb = pynetbox.api('http://127.0.0.1:8000', token='04a219fcfbef4bd7e874ea9ab191a4822b7d1edc') try: # Retrieve all networks from NetBox networks = nb.ipam.prefixes.all() # Process the networks for network in networks: print(f"Network ID: {network.id}") print(f"Prefix: {network.prefix}") print(f"Site: {network.site}") print('---') except pynetbox.core.query.RequestError as e: print(f"An error occurred: {e}") |
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
(venv) osboxes@osboxes:~/scripts/django-new_networks$ /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/venv/bin/python /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/pynetbox_examples/pynetbox_getall_networks.py Network ID: 1 Prefix: 172.17.10.0/24 Site: UK1 --- Network ID: 2 Prefix: 172.17.20.0/24 Site: UK1 --- Network ID: 3 Prefix: 172.17.30.0/24 Site: UK1 --- Network ID: 4 Prefix: 172.17.40.0/24 Site: UK1 --- Network ID: 5 Prefix: 172.18.10.0/24 Site: US1 --- Network ID: 6 Prefix: 172.18.20.0/24 Site: US1 --- Network ID: 7 Prefix: 172.18.30.0/24 Site: US1 --- Network ID: 8 Prefix: 172.18.40.0/24 Site: US1 --- Network ID: 9 Prefix: 172.19.10.0/24 Site: US2 --- Network ID: 10 Prefix: 172.19.20.0/24 Site: US2 --- Network ID: 11 Prefix: 172.19.30.0/24 Site: US2 --- Network ID: 12 Prefix: 172.19.40.0/24 Site: US2 --- |
Adding to NetBox through PyNetBox
This script is to add 10 VLANs to each site from VLAN 100-109.
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
import pynetbox # Instantiate a NetBox API object nb = pynetbox.api('http://127.0.0.1:8000', token='04a219fcfbef4bd7e874ea9ab191a4822b7d1edc') try: # Define the VLAN range and site names vlan_start = 100 site_names = ['UK1', 'US1', 'US2'] # Create VLANs in each site for i, site_name in enumerate(site_names): site = nb.dcim.sites.get(name=site_name) for j in range(10): vlan_id = vlan_start + j vlan_data = { 'vid': vlan_id, 'name': f'{vlan_id}{site_name}_automation_test', 'site': site.id, # Add any additional VLAN fields here } vlan = nb.ipam.vlans.create(vlan_data) print(f"Created VLAN {vlan.id} in Site {site_name}: VLAN ID {vlan.vid}") except pynetbox.core.query.RequestError as e: print(f"An error occurred: {e}") |
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
(venv) osboxes@osboxes:~/scripts/django-new_networks$ /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/venv/bin/python /home/osboxes/scripts/django-new_networks/pynetbox_examples/pynetbox_createvlans.py Created VLAN 43 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 100 Created VLAN 44 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 101 Created VLAN 45 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 102 Created VLAN 46 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 103 Created VLAN 47 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 104 Created VLAN 48 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 105 Created VLAN 49 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 106 Created VLAN 50 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 107 Created VLAN 51 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 108 Created VLAN 52 in Site UK1: VLAN ID 109 Created VLAN 53 in Site US1: VLAN ID 100 Created VLAN 54 in Site US1: VLAN ID 101 Created VLAN 55 in Site US1: VLAN ID 102 Created VLAN 56 in Site US1: VLAN ID 103 Created VLAN 57 in Site US1: VLAN ID 104 Created VLAN 58 in Site US1: VLAN ID 105 Created VLAN 59 in Site US1: VLAN ID 106 Created VLAN 60 in Site US1: VLAN ID 107 Created VLAN 61 in Site US1: VLAN ID 108 Created VLAN 62 in Site US1: VLAN ID 109 Created VLAN 63 in Site US2: VLAN ID 100 Created VLAN 64 in Site US2: VLAN ID 101 Created VLAN 65 in Site US2: VLAN ID 102 Created VLAN 66 in Site US2: VLAN ID 103 Created VLAN 67 in Site US2: VLAN ID 104 Created VLAN 68 in Site US2: VLAN ID 105 Created VLAN 69 in Site US2: VLAN ID 106 Created VLAN 70 in Site US2: VLAN ID 107 Created VLAN 71 in Site US2: VLAN ID 108 Created VLAN 72 in Site US2: VLAN ID 109 |
Using the API Documentation
It’s all well and good, me showing different test scripts that do very little. Pynetbox is a wrapper for the NetBox API. It is simple to use and to see what you want you can use the NetBox API documentation, http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/
To successfully use this, decide what you want to see. Say for example, you want to see all the attributes of the sites. Well they’re under dcim, go into that and then find sites. From here, the full list of attributes is shown for what is already configured in NetBox. Each of these attributes can be called.
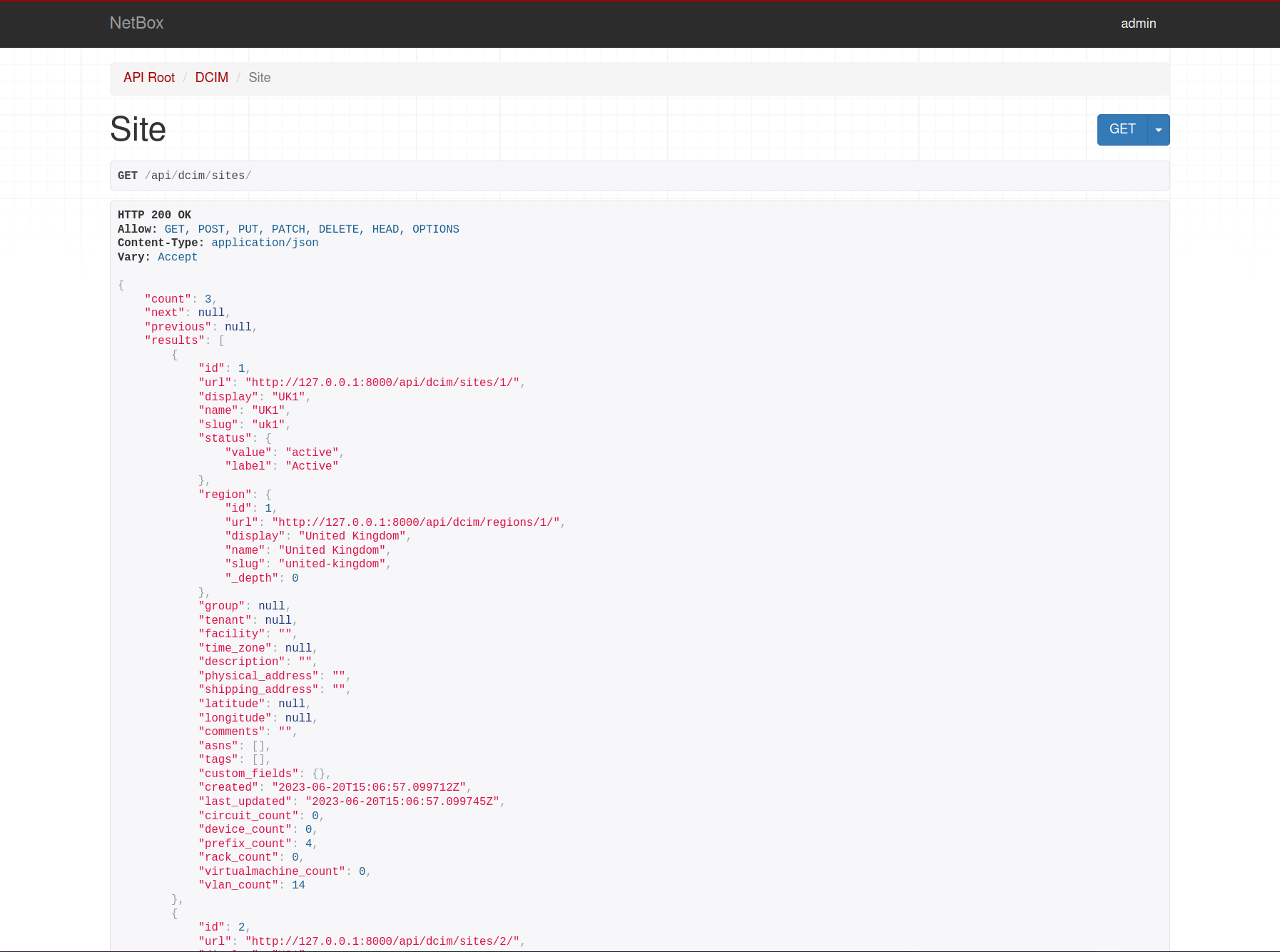
How things line up between the API documentation and Pynetbox can be seen with the snippet of code below. The attributes are called are .id, .name and .slug all can be easily seen above in the API documentation.
|
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
# Retrieve all sites from NetBox sites = nb.dcim.sites.all() # Process the sites for site in sites: print(f"Site ID: {site.id}") print(f"Name: {site.name}") print(f"Slug: {site.slug}") print('---') |
